Zoonosis is when animals pass diseases to humans. Read expert advice on what to watch for, the risks of animal diseases transmitted to humans, and how to prevent them.
Here, Elanco Animal Health veterinarian Dr. Zach Miller discusses diseases humans can get from cats or dogs and how to prevent zoonosis from happening.
For those who don't know, what is zoonosis?
Dr. Miller: Zoonosis is when a disease is passed from animals to humans, and pet owners may be at greater risk than others. While this may sound scary, with proper precautions you can greatly lower your risk of acquiring a disease from your pet.
Does zoonosis work both ways - can humans transmit diseases to their dogs or cats?
Dr. Miller: In rare situations, people can actually pass diseases on to their pets. For example, in 2009 during an influenza flu outbreak, several pets (dogs, cats and ferrets) were infected from their sick owners. Other examples include tuberculosis and giardia. It's called reverse zoonosis or anthroponosis - and it's pretty uncommon.
What are some examples of diseases humans can get from cats and dogs through zoonosis?
Dr. Miller: There are several different ones. Worms is a big one - cats and dogs can become infected with roundworms, hookworms and tapeworms. Roundworms and hookworms lay thousands of eggs that travel through feces and end up in the soil and the grass. This is especially risky for children, because when they play outside they often put their hands to their mouths, accidentally ingesting the infective worm eggs and becoming infected.
Tapeworms are carried by fleas and when a human has close contact, such as lying on the couch with their pet, they can accidentally ingest the fleas. They're so tiny that humans won't even realize it's happened. You can easily prevent fleas on your pet with an effective flea control product.
Ringworm is also one of the diseases humans can get from animals, especially cats. It's a fungus that grows on skin that cats can pass on through close skin-to-skin contact. If your cat has this, they will likely have a rough, hairless spot on their body.
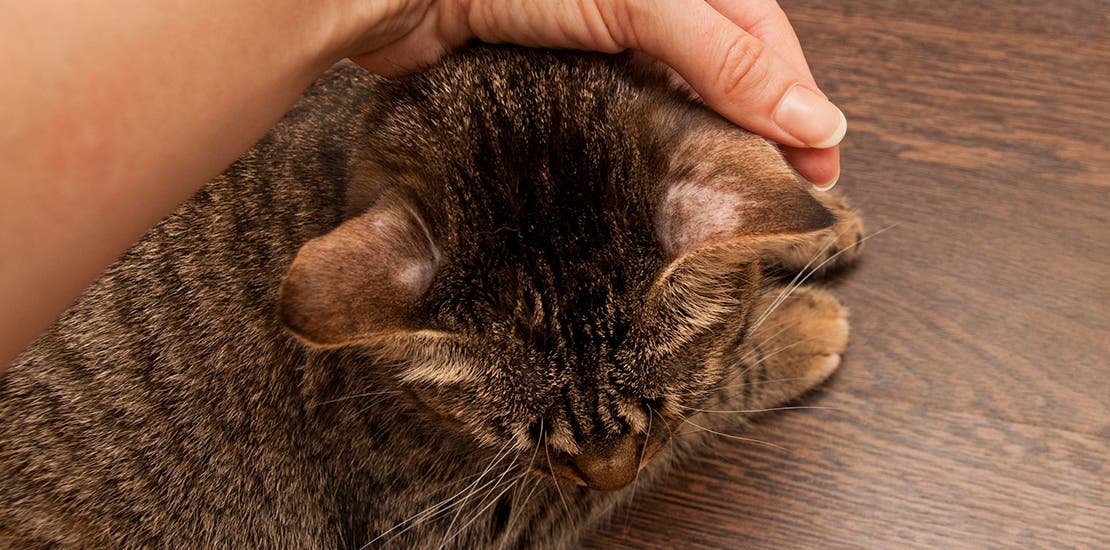

You mentioned ringworm is very common for cats. Are there any other diseases specific to cats or dogs that can be passed along via zoonosis?
Dr. Miller: Cat scratch fever comes from bacteria that lives in fleas called Bartonella. When the fleas defecate, the bacteria gets on the cat, which can transfer to the cat's claws. If that cat scratches you, then the bacteria goes directly into the wound. When you get cat scratch fever, the wound will get swollen and you could also get a fever and hives.
Sarcoptic mange is one of the dog diseases transmitted to humans. It's a microscopic mite that burrows under the skin. If people have close contact with a dog, then this mite can transfer over to the person's skin. It causes extreme itching and rashes along the bodies of both dogs and people.
Which diseases should pet owners be most concerned about?
Dr. Miller: Rabies would certainly be high on the list, simply because of the devastating impact it has on humans. If a person gets bitten by a rabid animal, such as a skunk or raccoon, they in all likelihood will die unless they get immediate medical intervention. This is why it's required by law for pets to have rabies shots. Animals with rabies often act aggressively, display bizarre behavior or show neurological signs.
Many people rescue homeless cats or dogs. If the animals have been living on the streets, what are some of the diseases these animals are most likely to carry that can be transmitted to humans?
Dr. Miller: Since the animal has been living outdoors, they are at a great risk for all of these diseases. Whenever you adopt a pet - be it from the streets, a shelter, a pet store or a breeder - you should take them to the veterinarian immediately. The veterinarian will be able to identify any issues or concerns as well as provide education, such as flea and tick prevention.
Should people who have other pets - such as reptiles and birds - be concerned about other diseases that can be transmitted through zoonosis?
Dr. Miller: Lizards, turtles and other reptiles, as well as small mammals like hedgehogs, carry salmonella. This is why petting zoos have so many hand-washing stations. Pet birds can carry a respiratory disease called psittacosis that can be transmitted to humans through close contact with feathers, dander or other secretions. It's sometimes called "bird fever" or "parrot fever," and the symptoms are fever, chills, and eye irritation with discharge.
What is the best way to prevent diseases you can get from your cat or dog?
Dr. Miller: A lot of the time, it simply comes down to good hygiene. Wash your hands after being outside and make sure your children do so as well. Sandboxes and playgrounds are a big deal. The sand and gravel look like cat litter and stray cats can think it's a big litter box, so teach children not to put their hands in their mouths (I know that can be difficult to enforce). Intestinal worm eggs live in the soil and there can be other microscopic worms lying on the grass and in sand that can get into your skin and you don't even realize it. Because of this, do not walk barefoot or lie in areas that are known to be common animal soiling locations, and make sure to always pick up pet waste as soon as possible. The main message is to be careful when handling animals and always wash your hands.